How to connect p5js to an arduino to sense or control the real world
How to control or measure something in the real world with p5js and a Arduino (or esp32 etc.)
For the Artificial Intelligence workshop at Humtek spring 2025
Until recently, it was difficult to control hardware from javascript/p5js in a browser. Now however it is reasonably easy, as hte browser Chrome supports javascript talking to a hardware serial port. (other browsers may or may not work)
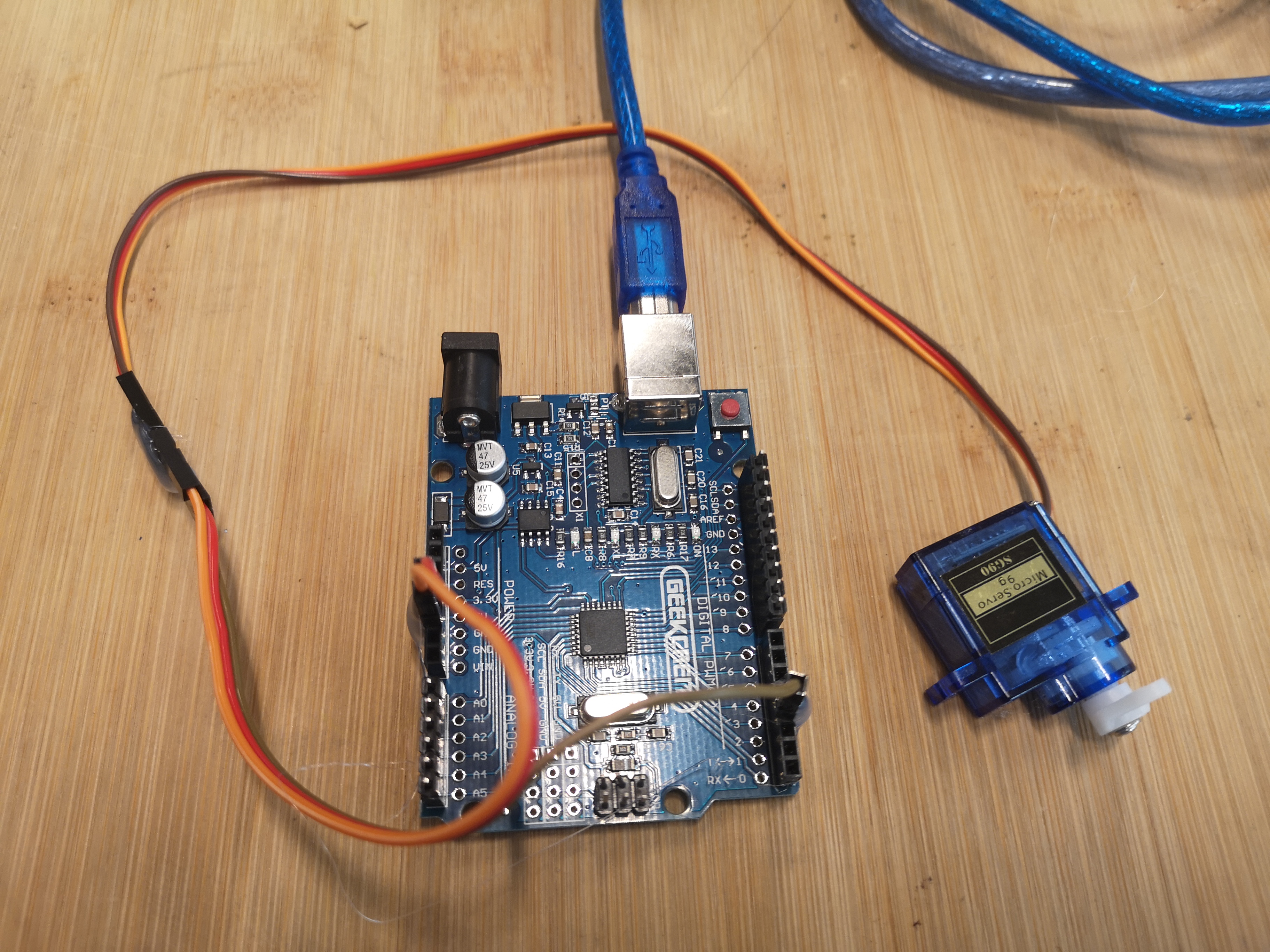 In this example, connect a servo to pin 3, 5V and GND
In this example, connect a servo to pin 3, 5V and GND
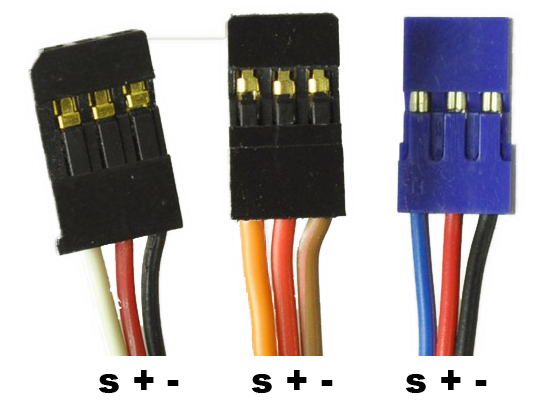
Pinout/colours (http://www.pitch-play.nl/tips-and-tricks/servo-wires/)
To control or sense something in the real world from p5js, you need four things:
1) p5js sketch (below)
2) Arduino sketch (below)
3) Arduino compatible board (e.g. esp32, esp8266 also work fine)
4) Actuators or sensors to connect to the arduino board. (in this example a servo.
This solution is as simple as possible and does not use higher level abstraction layers like firmata, json etc.
p5js code:
(modified from https://learn.hobye.dk/kits/iot-tutorial ESP32/Arduino SERIAL to p5 (Directly))
Here:
https://editor.p5js.org/nicolasp/sketches/qQt7MMBt1
Or here:
// p5js code to send data to Arduino
let serialAvaliable = false;
let serialInput = "";
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
print("click on sketch canvas and press c to select serial port and connect")
}
function keyPressed() {
if (key == "c") {
serialConnect();
}
}
var timer = 0;
var variable1 = 20;
var variable2 = 0;
function draw() {
background(220);
// prints the serial input buffer when the serialAvaliable flag is true
if (serialAvaliable) {
serialAvaliable = false;
print(serialInput);
serialInput = "";
}
//Send data to the arduino every 2 seconds
//- if data from Arduino shows up in the console it means that the arduino recieved it and returned some sensor values
if (millis() - timer > 2000) {
timer = millis();
variable1 = variable1 + 5;
serialWrite(variable1);
serialWrite(",");
serialWrite(variable2);
serialWrite("\n");
}
}
// XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
// SERIAL COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS BELOW
// XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
let port;
let reader;
let inputDone;
let outputDone;
let inputStream;
let outputStream;
let portIsOpen = false;
async function serialListen() {
if (portIsOpen) {
while (true) {
const { value, done } = await reader.read();
if (value) {
serialAvaliable = true;
serialInput = serialInput + value;
}
if (done) {
console.log("[readLoop] DONE", done);
reader.releaseLock();
break;
}
}
}
}
async function serialConnect() {
if (navigator.serial) {
port = await navigator.serial.requestPort();
await port.open({ baudRate: 9600 });
const decoder = new TextDecoderStream();
inputStream = decoder.readable;
inputDone = port.readable.pipeTo(decoder.writable);
reader = inputStream.getReader();
const encoder = new TextEncoderStream();
outputDone = encoder.readable.pipeTo(port.writable);
outputStream = encoder.writable;
portIsOpen = true;
print("Port is open");
serialListen();
} else {
print("Serial not compatible with the browser you are using :/");
}
}
function serialWrite(line) {
if (portIsOpen) {
// CODELAB: Write to output stream
const writer = outputStream.getWriter();
writer.write(line);
writer.releaseLock();
}
}
Arduino sketch code:
// p5js sketch should send data like 40,1\n (=newline)
// this should move servo to 40 degrees and make LED on pin 2 (if exists) light up
// Arduino sends data like 130,400\n (=newline), these are the values of the analog in pins
// so this sketch supports 4 things, you probably only need one of them
// but the data still needs to be in this format: 20,0\n
// if you send any other data, you may need to reboot the arduino, as it does not handle other data formats
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo. Twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position. May be 0 to 180
int extraLedPin = 2;
void setup() {
// Start serial communication so we can send data over the USB connection from our p5js sketch
Serial.begin(9600);
myservo.attach(3); // attaches the servo on pin 3 to the servo object
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(extraLedPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// wait for data from p5 before doing something
while (Serial.available()) {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // led on while receiving data
int variable1 = Serial.parseInt();
int variable2 = Serial.parseInt();
if (Serial.read() == '\n') {
if(variable1 >= 0 && variable1 <= 180){
myservo.write(variable1); // tell servo to go to position in variable1
}
digitalWrite(extraLedPin, variable2);
// This is how we send sensor data back to the p5 sketch
int sensor = analogRead(A0);
delay(5);
int sensor2 = analogRead(A1);
delay(5);
Serial.print(sensor);
Serial.print(',');
Serial.println(sensor2);
}
}
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);
}